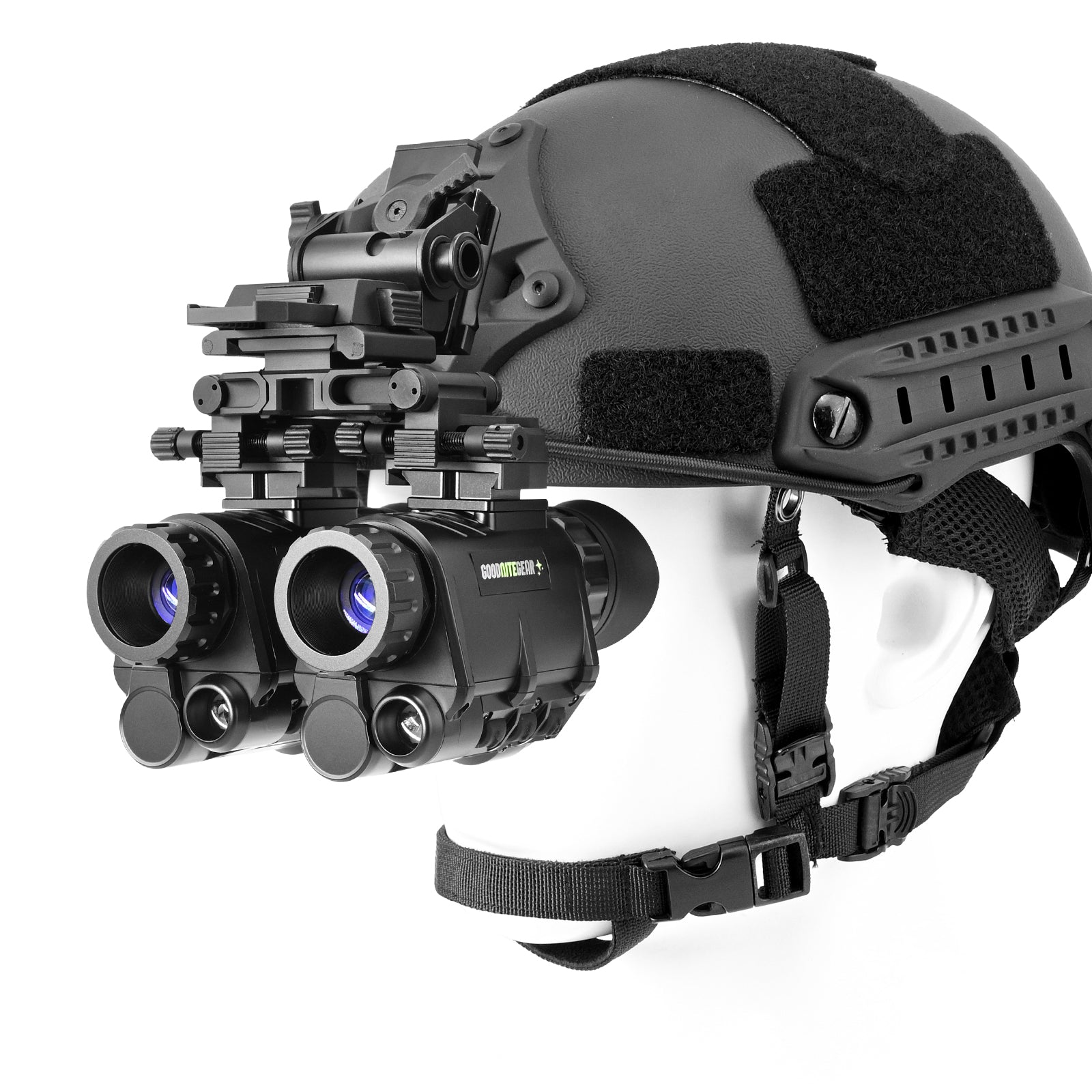
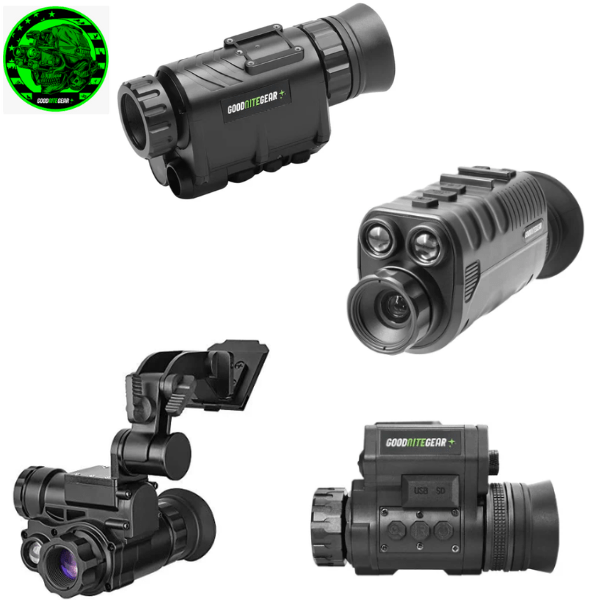
Suppose that you are walking in a thick forest covered in dark with just the moon and stars as light sources. Your eyesight will be adversely affected in such an environment. Before trying out this adventure, exploring the different types of night vision goggles (NVGs) is helpful in this situation.
NVGs improve vision in low light. These devices are equally important for adventurers and professionals whose tasks require working in densely dark nights.
Some of you may be unaware of the basics while exploring the different types of night vision goggles. Each NVG has its own technology, uses, and drawbacks.
Therefore, Good Nite Gear Shop is here to help you comprehend the fundamental technologies that underpin night vision so you can make the best investment in this regard.
The Fundamentals of Night Vision Technology
Before exploring their different types, learning about the technology underlying the various NVGs is mandatory. There are four primary ways that night vision operates:
Image Intensification
This is the most conventional and widely used approach. To create a viewable image, image intensification gathers ambient light, such as moonlight or stars, and amplifies it hundreds of times.
Thermal Imaging
Light is not necessary for thermal imaging. Instead, it picks up heat, or infrared (IR) radiation, released by objects.
Active Illumination
This technology combines an IR light source with picture intensification. This source is undetectable to the human eye but detectable by NVGs. It is only visible with night vision. However, it functions similarly to a flashlight in the dark.
Digital Night Vision
Digital sensors, like those in cameras, are used in digital night vision instead of analog intensification. These divides depend on CMOS or CCD sensors to convert light into a digital signal.
Get NVG50 Digital Night Vision Binocular now!
Exploring the Different Types of Night Vision Goggles
Now you know how night vision technology works, start learning about the primary NVG types based on their generation and purpose.
Generation 1 Night Vision Goggles
Gen 1 NVGs were originally released in the 1960s and became widespread in the 1970s and 1980s. They require ambient light to work and employ simple image intensification.
Pros
-
Most economical choice.
-
Easy to carry and operate.
Cons
-
Lower-resolution, grainy pictures.
-
Poor performance in extremely low-light conditions and a limited range.
Ideal Use
Gen 1 NVGs are best for outdoor activities such as:
-
Hiking
-
Camping
-
Simple wildlife observation
Buy NVG40 Pro Digital Night Vision Monocular.
Generation 2 Night Vision Goggles
The microchannel plate used in Gen 2 NVGs greatly improves light amplification and image quality.
Pros
-
Clearer and brighter images than Gen 1.
-
Enhanced functionality in dimly lit environments.
Cons
-
More costly than Gen 1.
-
Not as sophisticated as models from Generations 3 and 4.
Ideal Use
Gen 2 NVGs are best to use in:
-
Law enforcement
-
Security guards
-
Serious outdoor enthusiasts
Generation 3 Night Vision Goggles
Gallium arsenide photocathodes are used in Gen 3 NVGs to increase light sensitivity and clarity significantly.
Pros
-
Excellent quality of images.
-
Long lifespan and outstanding performance at extremely low light levels.
Cons
-
Expensive, frequently costing between $2,000 and $4,000.
-
Has to be handled carefully because of its delicate parts.
Ideal Use
Gen 3 NVGs are best used by:
-
Tactical operators
-
Professional surveillance teams
-
Military people
Generation 4 Night Vision Goggles
Gen 4 NVGs (or filmless NVGs) are the most advanced technology on the market. They have improved auto-gating and decreased noise for clearer photos.
Pros
-
Optimal performance in complete darkness and all light levels.
-
Decreased distortion and very bright and clear images.
Cons
-
Quite expensive, frequently more than $5,000.
-
More delicate when exposed to intense light.
Ideal Use
Gen 4 NVGs are best used in:
-
Governmental organizations
-
Special forces
-
Elite military formations
Thermal Imaging Goggles
Thermal goggles are effective in total darkness or through visual obstacles because they sense heat rather than light.
Pros
-
Operates in complete darkness and unfavorable environments like fog or smoke.
-
Detects people and warm-blooded animals with ease.
Cons
-
More costly in general.
-
Less detail than the intensified picture.
Ideal Use
Thermal imaging goggles are ideally used for:
-
Firefighting
-
Military and law enforcement applications
-
Search and rescue missions
Digital Night Vision Goggles
Digital night vision goggles collect and analyze light using digital sensors. Several versions include playback, recording, and even Wi-Fi or app connectivity.
Pros
-
Frequently offers color imaging.
-
Able to capture pictures and record video.
-
Economical for average customers.
Cons
-
Negative performance in low light than analog devices.
-
Lower battery life and bulkier designs.
Ideal Use
Digital NVGs are best used for:
-
Tracking animals
-
Home security
-
Recreational outdoor pursuits
The Bottom Line
Exploring the different types of night vision goggles helps you buy the best one. From the most basic to advanced equipment, each type of gadget has its plus and minus points. Make the best decision by considering your project needs and budget.
Shop the best night vision goggles for the money now!